ArrayList class :
- Resizable Array or growable array.
- The underlined datastructure resizable and growable array.
- Duplicates are allowed.
- Insertion order is preserved.
- Heterogeneous objects are allowed(Except Tree Set and Tree Map everywhere heterogeneous objects are allowed).
- Null insertion is possible.
CONSTRUCTOR:
- ArrayList l = new ArrayList():- Creates an empty ArrayList object with default initial capacity 10.Once ArrayList reaches its max capacity a new ArrayList will be created.
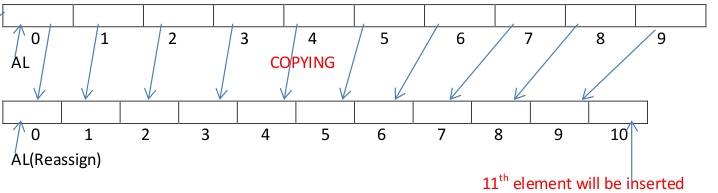
- After copying all the data into another arraylist garbage collector will de-allocate the first arraylist memory.

New Capacity = [ Current Capacity * 3/2 ] + 1
- ArrayList l = new ArrayList(int initialCapacity);
- ArrayList l = new ArrayList(Collection c);
Example for Arraylist:
Import java.util.*;
Class ArrayListDemo{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList l = new ArrayList();
L.add(“A”);
l.add(10);
l.add(“A”);
l.add(null);
System.out.println(l);// [A,10,A,null]
l.remove(2);
System.out.println(l);// [A,10,null]
l.add(“2”,”m”);
l.add(“n”);
System.out.println(l); // [A,10,m,null,n]
}
}Note : We will get the output in brackets. Because object reference internally its going to implemented as toString method.
When Arraylist is best and worst choice?
- Arraylist is the best choice if our requirement is retrieval operation(Because Arraylist implements RandomAccess interface).
- ArrayList is the worst choice if our requirement is insertion or deletion in the middle(Because shift operation are required).

l.add(1,”m”);
l.remove(1);
How to get Synchronized version of ArrayList object?
By default ArrayList is object is non-synchronized but we can get synchronized version of ArrayList by using collection class SynchronizedList() method.
NON-SYNCHRONIZED:
ArrayList l1 = new ArrayList();
SYNCHRONIZED:
List l = Collections.SynchronizedList(l1);
Point : Similarly we can get synchronized version of Set, Map objects by using the following methods of collection class