Function scope and Block scope concepts are used with variable acceptability and availability. Function Scope variable is declared inside a function, it is only accessible within that function and cannot be used outside that function.
Block Scope variables declared inside the if statement or switch conditions block or inside for or while loops are accessible within that particular condition or loop. To be concise the variables declared inside the curly braces are called within the block scope.
There are also keywords used:
The let and var are used to the scope of a variable defined with let are limited to the block in which it is declared while the variable declared with var has the global scope.
Function scope and Block scope in JavaScript example
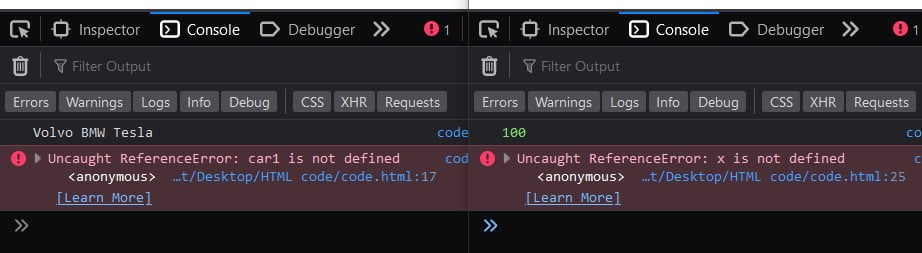
Simple example code.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
// function scope
function myFunction() {
// Function Scope variables
var car1 = "Volvo";
var car2 = "BMW";
var car3 = "Tesla";
console.log(car1,car2,car3)
}
myFunction();
console.log(car1,car2,car3)
// bock scope
{
let x = 100;
console.log(x)
}
console.log(x)
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
here’s a tabular representation of function scope and block scope in JavaScript:
| Scope Type | Declaration Keyword | Visibility | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Function Scope | var | Limited to the function where declared | |
| Block Scope | let and const | Limited to the block where declared | |
| Block Scope (ES6) | let and const | Limited to the block where declared |
Comment if you have any doubts or suggestions on this JS scope topic.
Note: The All JS Examples codes are tested on the Firefox browser and the Chrome browser.
OS: Windows 10
Code: HTML 5 Version