JavaScript null represents the intentional absence of any object value. Simple null means the absence of a value. You can assign null to a variable to denote that currently, that variable does not have any value but it will have later on.
If you wish to shred a variable of its assigned value, you can simply assign ‘null’ to it.
var myVar = null;Example null in JavaScript
Simple example code.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
const a = null;
console.log(typeof a);
console.log(a);
</script>
</body>
</html> Output:
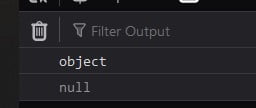
Difference between null and undefined
When checking for null or undefined, beware of the differences between equality (==) and identity (===) operators, as the former performs type-conversion.
typeof null // "object" (not "null" for legacy reasons)
typeof undefined // "undefined"
null === undefined // false
null == undefined // true
null === null // true
null == null // true
!null // true
isNaN(1 + null) // false
isNaN(1 + undefined) // trueDo comment if you have any doubts or suggestions on this JS null topic.
Note: The All JS Examples codes are tested on the Firefox browser and the Chrome browser.
OS: Windows 10
Code: HTML 5 Version