In Python, the expression “if boolean False” refers to using a boolean value of False as a condition in an if statement. The if statement allows you to execute a block of code only if a certain condition is true.
When the boolean value False is used as the condition in an if statement, the code block associated with the if statement will not be executed. This means that any code within the if block will be skipped.
Here’s an example:
flag = False
if flag:
print("This code will not be executed.")
else:
print("This code will be executed.")
In the above example, the variable flag is assigned the boolean value False. When the if statement is evaluated with flag as the condition, it evaluates to False. As a result, the code block under the if statement is not executed, and the code block under the else statement is executed instead.
Python if boolean False example
Here’s an example that demonstrates the use of an if statement with a boolean condition that evaluates to False:
# A function to check if a number is positive
def check_positive(num):
if num > 0:
print(f"{num} is a positive number.")
else:
print(f"{num} is not a positive number.")
# Test the function
check_positive(5)
check_positive(-2)
check_positive(0)
Output:
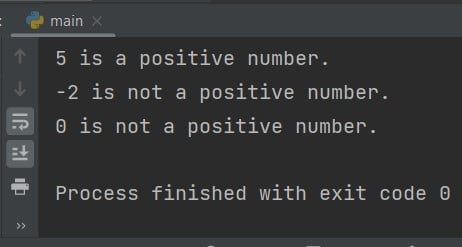
When we call the check_positive() function with different numbers, the output will vary based on whether the number is positive or not.
Do comment if you have any doubts or suggestions on this Python boolean topic.
Note: IDE: PyCharm 2021.3.3 (Community Edition)
Windows 10
Python 3.10.1
All Python Examples are in Python 3, so Maybe its different from python 2 or upgraded versions.